IJMS | Free Full-Text | Differential Protein Expression Profiles of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Following Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Direct and Indirect Lung Injury in Mice

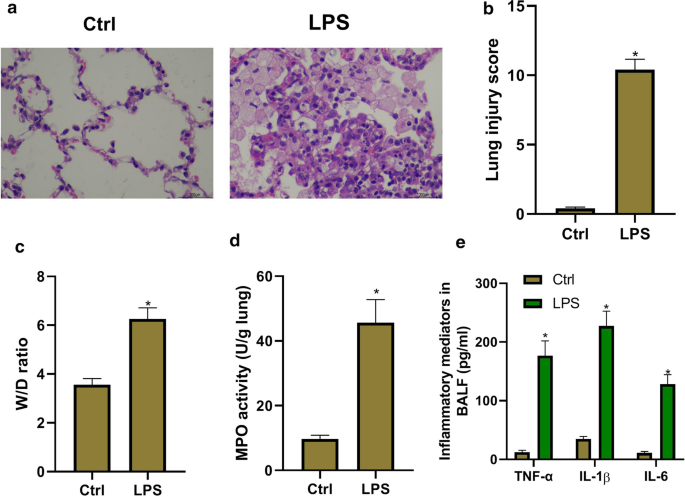
Chrysosplenol D protects mice against LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis via TLR4-MAPKs/NF-κB signaling pathways - Qinqin Zhang, Aozi Feng, Mengnan Zeng, Beibei Zhang, Jingya Shi, Yaxin
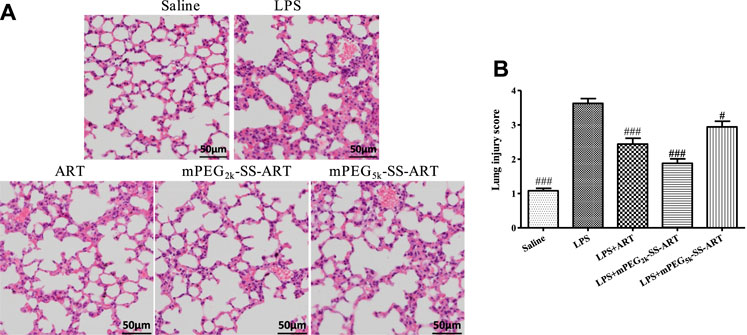
Frontiers | The Alleviation of LPS-Induced Murine Acute Lung Injury by GSH-Mediated PEGylated Artesunate Prodrugs

Euphorbia factor L2 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and inflammation in mice through the suppression of NF-κB activation - ScienceDirect

Monitoring lung injury with particle flow rate in LPS‐ and COVID‐19‐induced ARDS - Stenlo - 2021 - Physiological Reports - Wiley Online Library
Receptor Interacting Protein 3-Mediated Necroptosis Promotes Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Mice | PLOS ONE

Fucoidan inhibits LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice through regulating GSK-3β-Nrf2 signaling pathway | SpringerLink

LPS-induced lung inflammation. Mice were injected intratracheally with... | Download Scientific Diagram
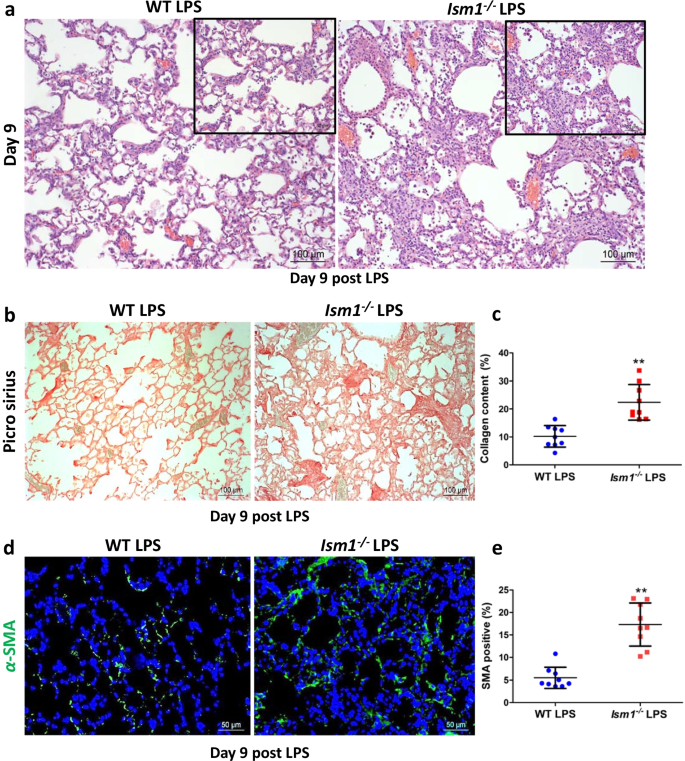
ISM1 suppresses LPS-induced acute lung injury and post-injury lung fibrosis in mice | Molecular Medicine | Full Text
Acyloxyacyl hydrolase promotes the resolution of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury | PLOS Pathogens

Glycyrrhizic Acid Alleviates Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE2) and Caveolin-1 Signaling Pathway | SpringerLink
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Trapa japonica Pericarp Extract Reduces LPS-Induced Inflammation in Macrophages and Acute Lung Injury in Mice

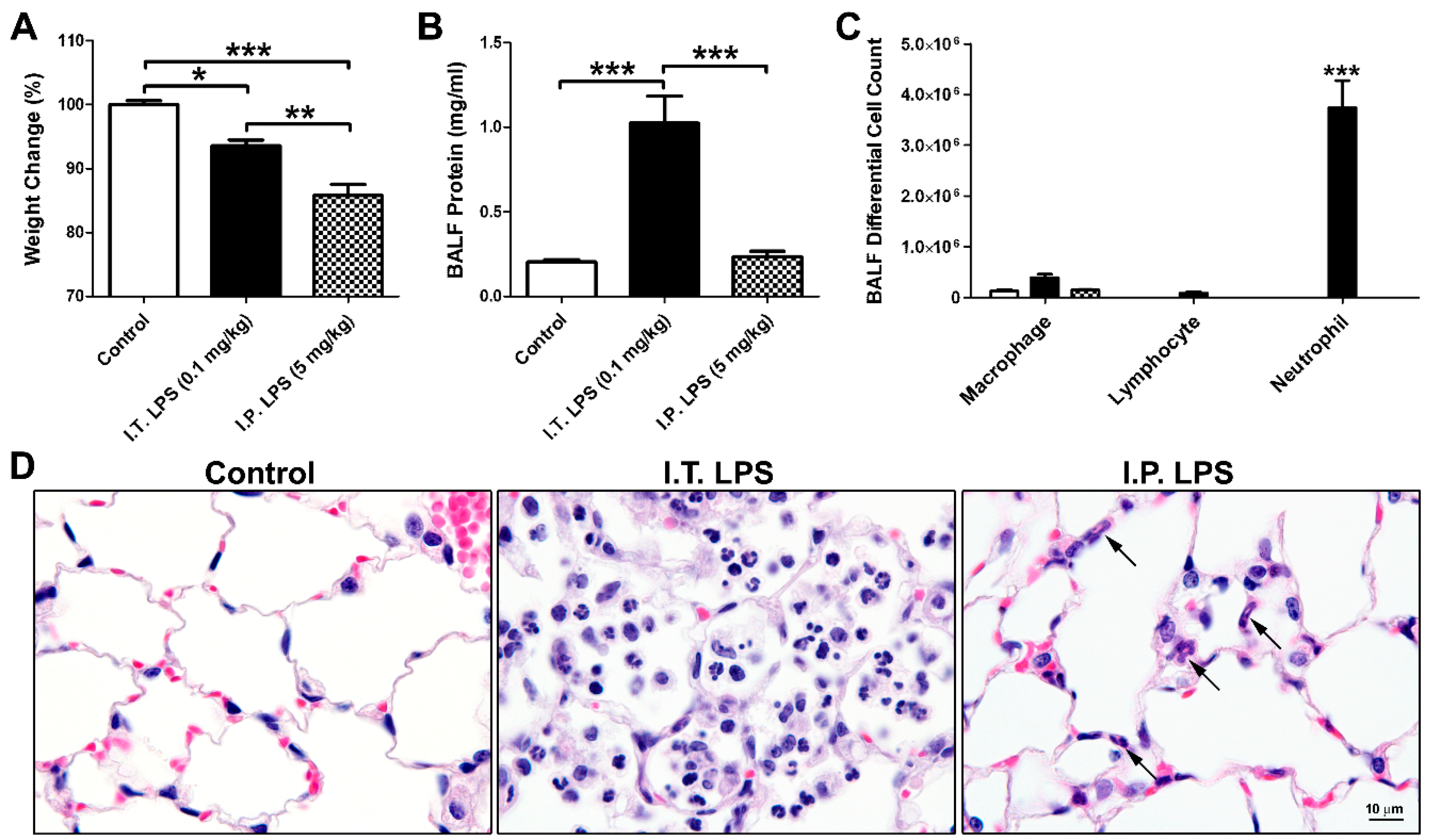
Comparison of direct and indirect models of early induced acute lung injury | Intensive Care Medicine Experimental | Full Text
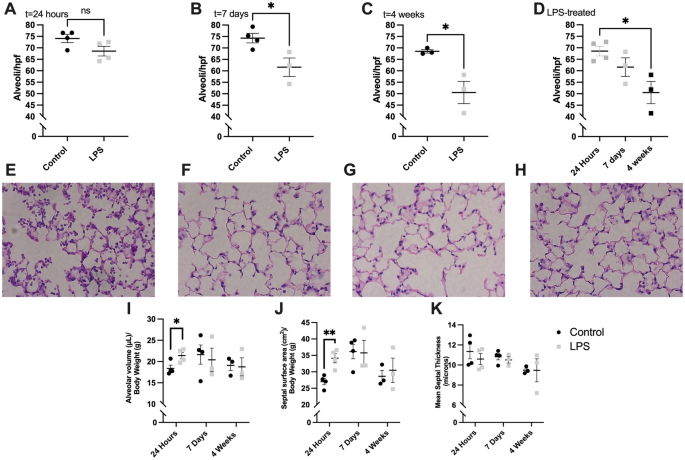
Lipopolysaccharide-induced murine lung injury results in long-term pulmonary changes and downregulation of angiogenic pathways | Scientific Reports
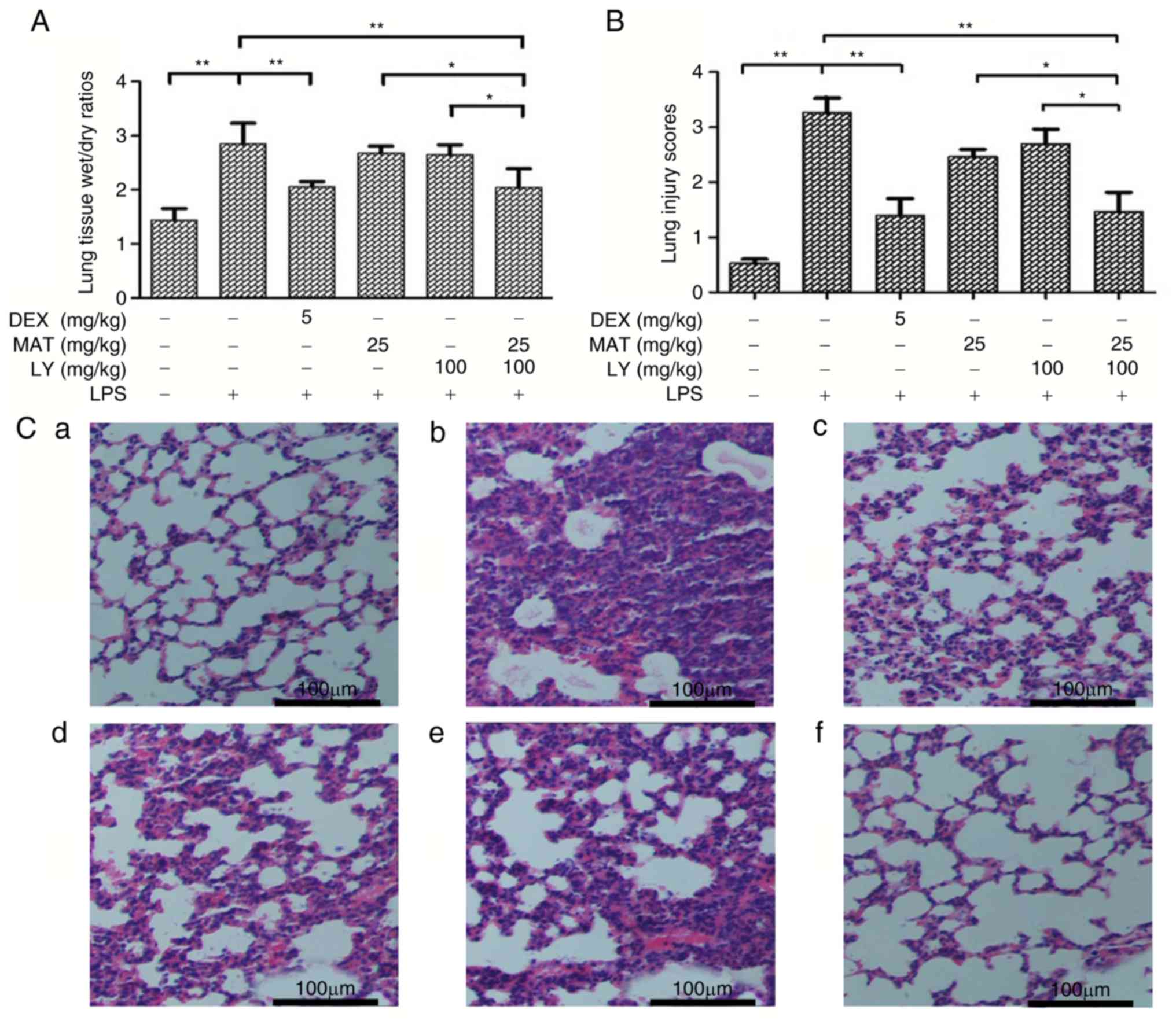
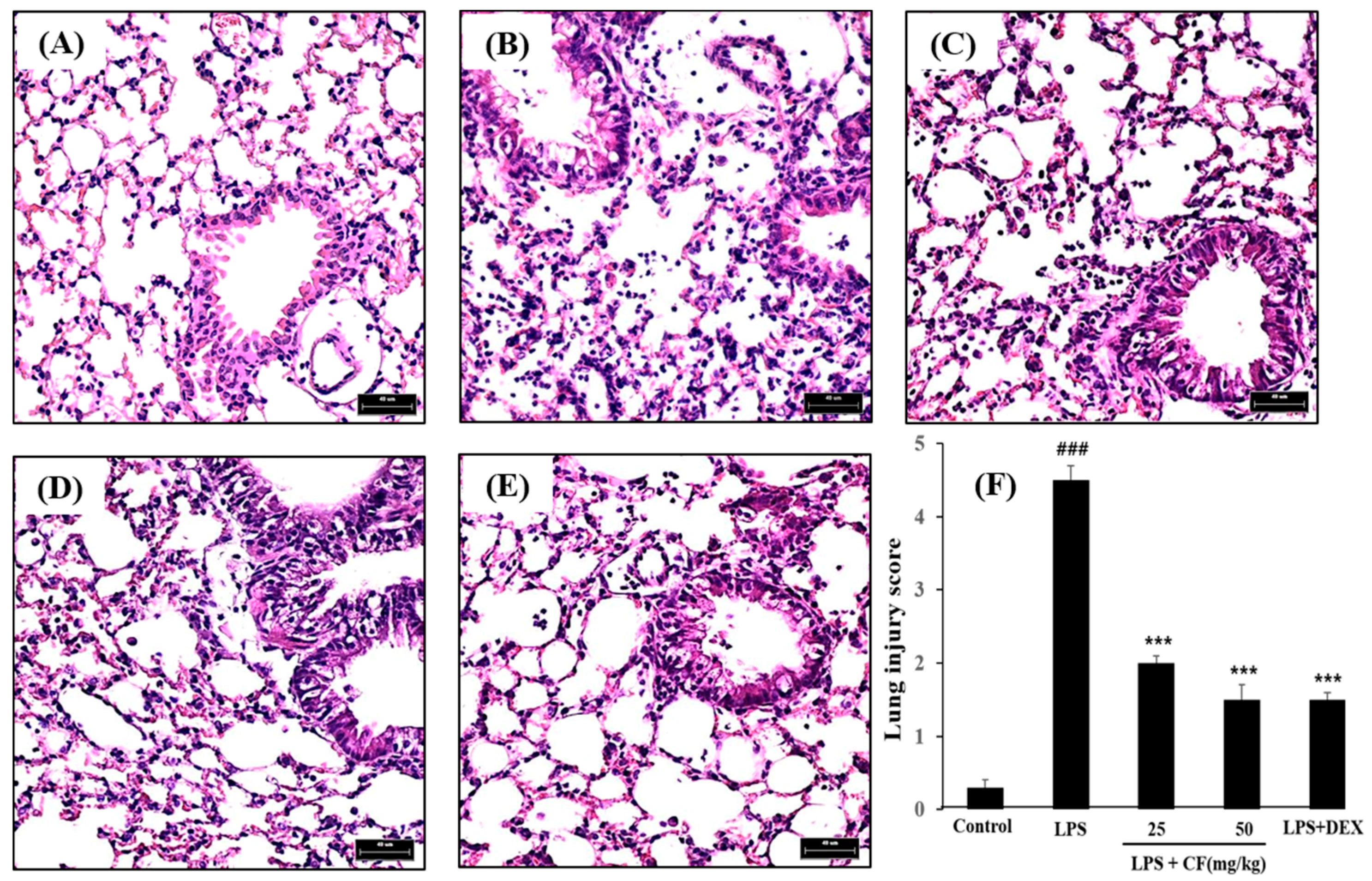
Synergistic protection of matrine and lycopene against lipopolysaccharide‑induced acute lung injury in mice
PARP-1 Inhibitor, DPQ, Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury through Inhibiting NF-κB-Mediated Inflammatory Response | PLOS ONE

LPS induces increased lung inflammation in adult versus neonatal mice.... | Download Scientific Diagram
Fucoxanthin attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88 signaling axis - Figure f8 | Aging

Lung inflammation promotes metastasis through neutrophil protease-mediated degradation of Tsp-1 | PNAS

Serum amyloid A promotes LPS clearance and suppresses LPS‐induced inflammation and tissue injury | EMBO reports
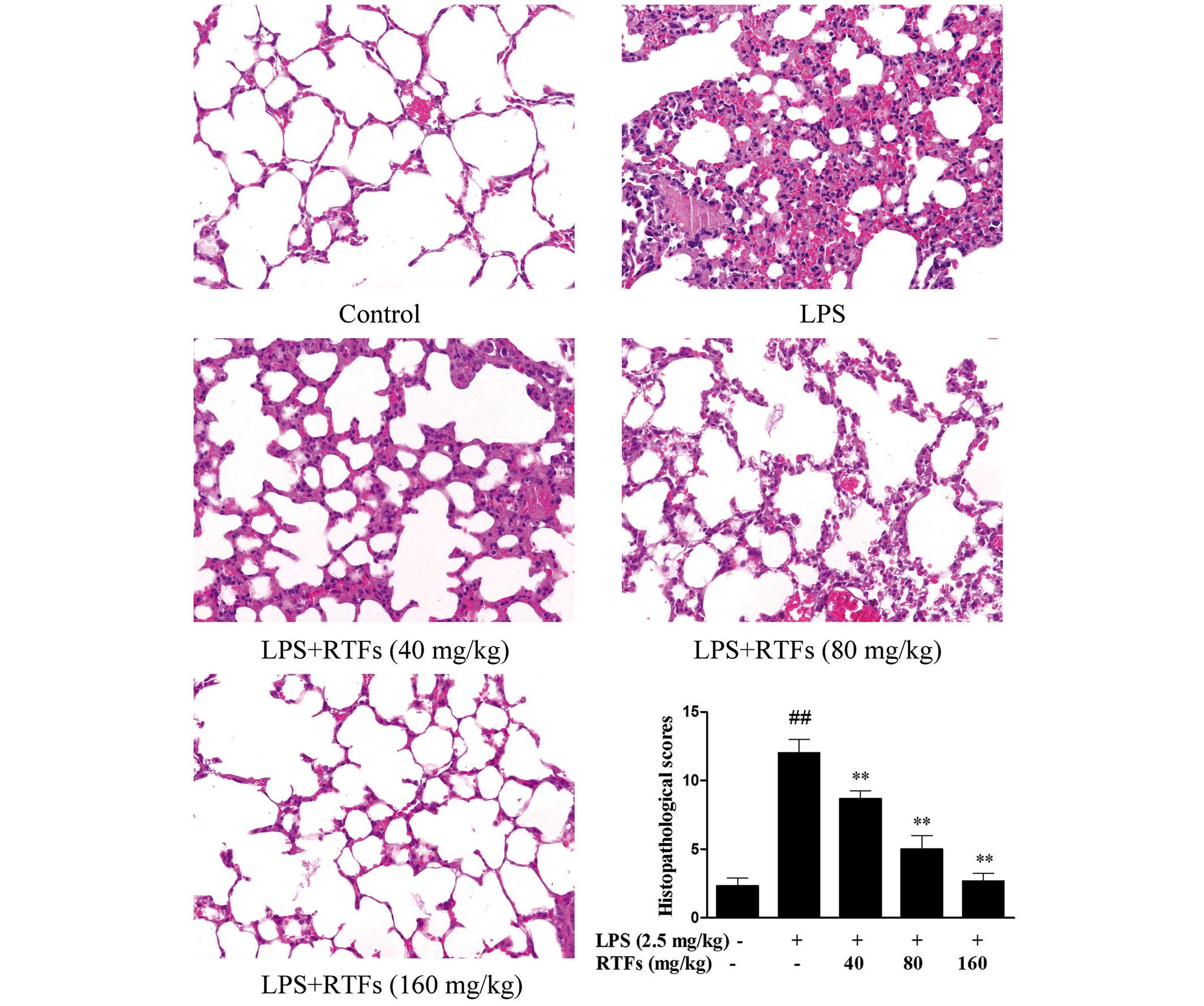
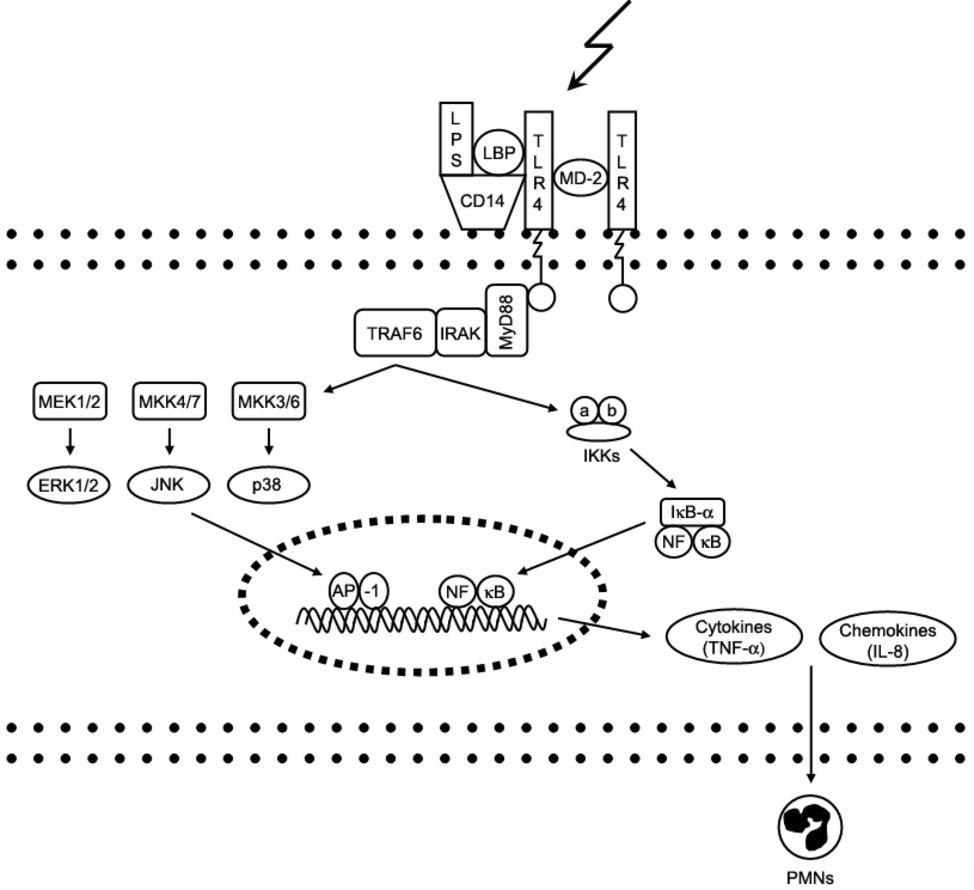
Flavonoids from Radix Tetrastigmae improve LPS-induced acute lung injury via the TLR4/MD-2-mediated pathway